A CSV file is the go-to solution for sharing data in a universal format. Discover more about this file format with practical tips on using CSV files.
CSV files, or Comma-Separated Values files, are a staple in data management and sharing. They store information in plain text, separating entries with commas. This simplicity makes them universally compatible and incredibly useful for tasks like importing data into software, creating databases, or sharing structured information.
What Is a CSV File and How Does It Work?
At its core, a CSV file is a straightforward way to organize data. Think of it as a simpler version of a spreadsheet where each row is a line of data, and each value is separated by a comma.
For example, a CSV file might look like this:
The CSV format is plain text, meaning it can be opened in anything from Excel to Notepad. It’s about keeping things simple and accessible regardless of operating system.
How To Create a CSV File
Making a CSV file is easier than you might think. Here’s how:
- Open a tool like Excel, Google Sheets, or any spreadsheet program.
- Enter your data in rows and columns.
- Each column represents a category, and each row is an entry.
- Once you're done, go to “File” > “Save As” or “Download” (depending on your tool).
- Choose the CSV format (usually labeled as .csv) and hit save.
And just like that, you've created your CSV file. Unless you’re creating it using a plain text editor, there’s no need to separate the data with a comma.
How To Use CSV Files in Everyday Tasks
CSV files work best when it comes to importing data into other applications. Here’s how they’re often used:
- In spreadsheets: Open your CSV file in Excel or Google Sheets to quickly view or edit the data. If you need to tidy up some data, this is the most efficient way to do it.
- For databases: Upload CSV files to import large datasets efficiently.
- Everyday examples: Import contact lists, product inventories, bank statements, or event schedules. It’s fast and fuss-free.
CSV Files vs. Other File Formats
CSV isn’t the only file format used for sharing data, though other file formats tend to be used for more specialized needs.
CSV vs. XLSX
CSV files are simpler than Excel files— they’re plain text with no bells or whistles. Excel files, on the other hand, offer advanced features like formulas and formatting, such as changing the font, using colors, or adding borders. Use CSV for compatibility and Excel when you need more functionality.
CSV vs. TXT
Both are plain text formats, but CSV files are structured with commas, making them perfect for tables. TXT files are freeform, ideal for unstructured text. Open a CSV file with Excel and all the data will be in separate columns. Do the same with a TXT file and all the data will be squashed into a single column.
CSV vs. JSON
CSV files are straightforward, while JSON organizes data in key-value pairs. JSON works better for complex datasets, with CSV better for simplicity and flat data.
CSV vs. XML
XML uses tags to structure data, making it more wordy but flexible. CSV files are cleaner and faster for simple data-sharing needs.
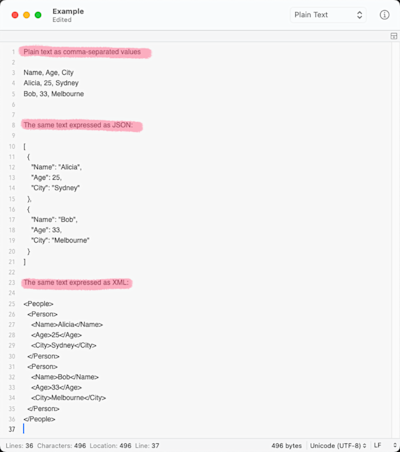
Example of the same data as CSV, JSON, and XML
It’s not that CSV is better than other file formats, but rather that other file formats are better suited to more specific uses.
Tips for Working With CSV Files
To avoid headaches, keep these tips in mind:
- Always double-check your data before saving in CSV format.
- Avoid using commas in entries; they can confuse the system.
- Use tools with built-in CSV support for seamless imports and exports.
Everything Else You Want To Know About CSV Files
What are the disadvantages of CSV files?
CSV files lack advanced formatting and can cause mistakes with misplaced commas. For instance, if a data entry contains multiple commas, it might get split incorrectly, causing errors. Additionally, CSV files don’t support formulas, charts, or cell styling, which limits their functionality for detailed reporting or analysis. They work best for importing data into other applications.
What is the purpose of a CSV file?
To store and share structured data in a universally accessible format. They’re especially useful when you need to move data between different software or systems. The plain text nature of CSV files ensures they remain lightweight and compatible across various platforms.
Why would you use a CSV file?
For its simplicity and compatibility across platforms. Unlike proprietary formats, CSV files don’t require specific software to open or edit them. Whether you’re working on a Mac, Windows, or even a mobile device, you can access CSV files without any hassle. This makes them a reliable choice for sharing data with others.
What is a CSV file commonly used for?
Sharing structured data like product inventories or event schedules. For example, e-commerce platforms often use CSV files to upload bulk product listings. Similarly, event planners can manage guest lists or schedules with ease.
Why use CSV instead of XLSX?
CSV files are smaller, simpler, and work across more systems. While Excel is great for advanced analysis, its complex features can make files bulky and harder to share. CSV files strip away these extras, focusing solely on the data, which is often all you need for importing or exporting between systems. Their smaller size also means they load faster and are easier to manage.
How do I open a CSV file?
Use a tool like Excel, Google Sheets, or even Notepad. Most modern operating systems allow you to double-click a CSV file to open it in a default program. For more control over how the data appears, you can import the file into spreadsheet software, where you can choose how the content is separated and displayed. It’s as simple as selecting “Open.”
Why use CSV instead of JSON?
CSV files are quicker for basic tasks, while JSON suits complex datasets. JSON’s structure is better for nested or hierarchical data, often used in web development or APIs. However, if you only need a simple table of information, CSV files are faster and easier to work with. They’re also more intuitive for non-technical users.
Is CSV or XML better?
CSV is better for simplicity and speed; XML offers more structure for complex data. XML can handle detailed metadata and relationships between data points, making it suitable for advanced applications. On the other hand, CSV’s lightweight nature makes it faster to process and easier to use in day-to-day tasks. Your choice will depend on the level of complexity your project requires.
